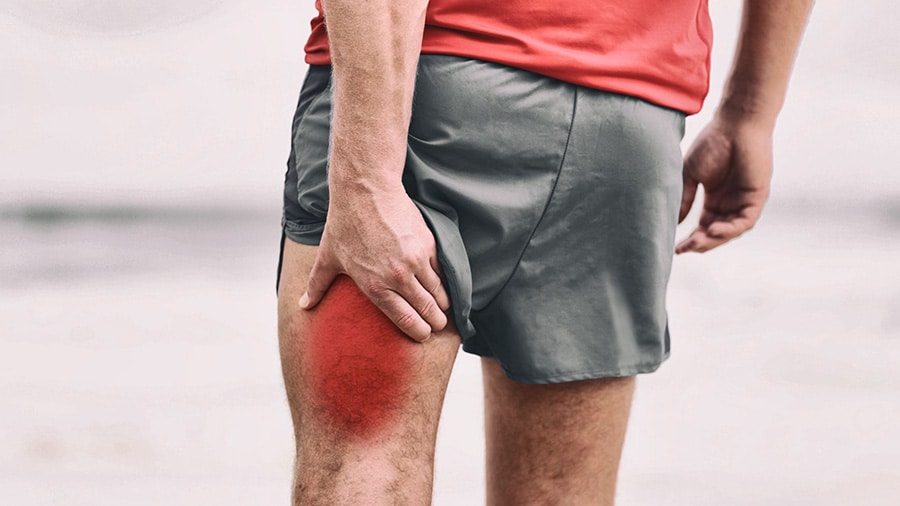
L'muscle elongation is a common injury among athletes. Unfortunately, it also affects weight trainers and fitness enthusiasts. While it may seem like a relatively minor injury at first glance, it should be treated quickly so as not to let the situation get worse. Find out everything you need to know to effectively treat this type of injury.
What is a muscle strain?
A muscle strain refers to a injury caused by an abnormal and excessive stretching of the fibers, without significant injury. In some cases, some small muscle fibers may be torn, but not seriously.
When a larger quantity of fibers in the affected muscle is ruptured, it is no longer an elongation, but rather a tear (otherwise known as a muscle strain). Stretching is therefore the first level of injury.
To learn more about the different injuries in bodybuilding, I invite you to read this article.
Muscle stretching usually occurs during a physical effort. It can affect almost all the muscles of the human body, from the thighs to the calves, including the glutes, hamstrings, adductors, biceps and triceps. In sportsmen and women, it is nevertheless the lower limbs that are most often impacted.

The causes of muscle strain are now well known. The lack of warm-up before practicing a sport is undoubtedly one of the most common.
Combined with too much effort, fatigue can also be the cause of this painful injury. Sudden movements during physical activity, muscular or postural imbalances and a lack of hydration are also factors to be taken into account. We will come back to this at the end of this article.
What are the symptoms of this injury?
Elongation is characterized by the sudden appearance of a pain It is less acute than a muscle tear, often compared to a "stab wound" by the athletes who suffer from it. It is however less acute than a muscle tear, often compared to "a stabbing" by the athletes who are victims.
This pain, more intense than that of a contracture, tends to disappear when the muscle group concerned is at rest. On the other hand, it is very present and perceptible during the palpationor when the muscle contracts.
A muscle strain does not result in a hematoma or edema (swelling) in the painful area. Unfortunately, the formation of a hematoma is most often a sign of a more serious muscle injury (tear or even total rupture).
The diagnosis of an elongation can be confirmed by theclinical examination a health professional such as a physiotherapist or a doctor. If in doubt, he or she may prescribe an ultrasound to make sure that the trauma is not more serious.
So what should you do if you have the symptoms of a muscle strain?
The treatment to follow for a muscle strain
At the time of injury
In case of sudden pain, the first thing to do is to stop your sports session immediately. Continuing your effort will aggravate the injury and increase the length of your future unavailability.
It is also important not to stretch. Indeed, stretching could amplify the micro-injuries that have occurred in the fibers.
The application of ice is strongly recommended as soon as the pain appears. Place an ice pack on the injured muscle group for 15 to 20 minutes. While waiting to consult a doctor, you can of course take an analgesic such as paracetamol to relieve the pain.
In the days following the trauma
Treating a muscle strain involves continuing to apply cold in the first few days (3 to 4 times). This is fundamental to reduce inflammation and accelerate healing.
Your doctor will tell you how long you will be unavailable. In addition, he will prescribe you anti-inflammatories non-steroidal (NSAIDs) to limit inflammation.
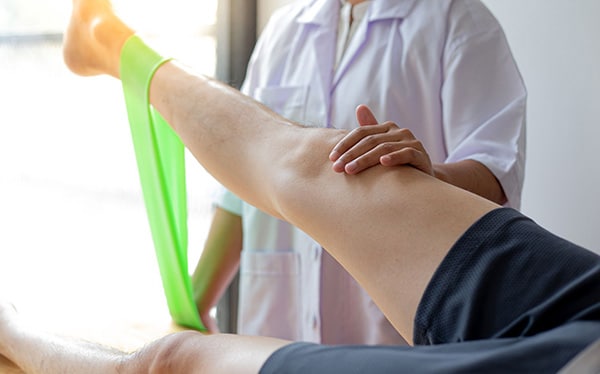
In addition, a good healing of the injury requires a rehabilitation phase. Whether you are an amateur or a high-level athlete, sessions of physical therapy are essential to strengthen and soften the muscle. This treatment will help you prevent recurrences.
Your physiotherapist will follow a well-defined protocol. In addition to muscle strengthening and stretching exercises, he or she may perform massages and offer electrostimulation and cryotherapy sessions.
The resumption of sport will be done gradually after a ten days on average. However, it is conditional on the total disappearance of the muscle pain.
If you had a leg injury, you will need to do several low-intensity jogging sessions before resuming normal cardio activity. If you have an upper body injury, the first few workouts of strength training should not be too brutal. Choose low loads for a few sessions to avoid relapse.
How to prevent muscle strains?
If you are involved in a physical activity such as weight training, you should pay particular attention to the prevention injuries. There are several elements that must be taken into consideration:
- the warm-up
- hydration
- food
- fatigue and sleep
- muscular reinforcement
- flexibility
Your warm-up
To avoid muscular injuries, it is above all essential to warm up before playing sports. A 10 to 20 minute warm-up will allow your body to warm up and your muscles and joints to perform the expected movements safely.
Don't know how to do it? Check out my sports coach's advice on how to warm up before a workout.
Your hydration and diet
During exercise, it is just as important to be sure you are moisturize to compensate for water loss due to perspiration.
More broadly, what you eat and drink on a daily basis has a direct impact on your health. To reduce the risk of injury, eat a healthy, balanced diet.
Sleep
The sleep and recovery play a major role.
If you are tired, it is best to adapt the intensity of your workouts by reducing, for example, the loads used or the number of repetitions performed.
Muscular strengthening
A muscle weakness is often the cause of repeated injuries. Through weight training, targeted strengthening is the best way to catch your weak points and fight against this phenomenon.
You want to benefit from a customized training program to finally reach your goals?
The relaxations
Regular injuries can also be caused by muscle stiffness. To perform well, your muscles must not only be strong. They must also be flexible to withstand the stresses imposed during training.
Remember to stretch several times a week to make yourself more flexible and limit muscular accidents.
Conclusion
A muscle strain is not a serious injury if it is taken seriously immediately. The application of ice, followed by physical therapy and a few days of rest will be enough to get rid of it. But be careful not to neglect your rehabilitation, otherwise you may relapse as soon as you resume your physical activity.