Physical activity and glycogen are intimately linked. Indeed, the practice of bodybuilding implies to realize intense efforts. To achieve this, your body and muscles need energy. This is the case, for example, when you do a series of squats or bench presses. But do you know how your body stores this energy? And how it releases it when you need it during training? That's precisely the role of glycogen.
What is glycogen?
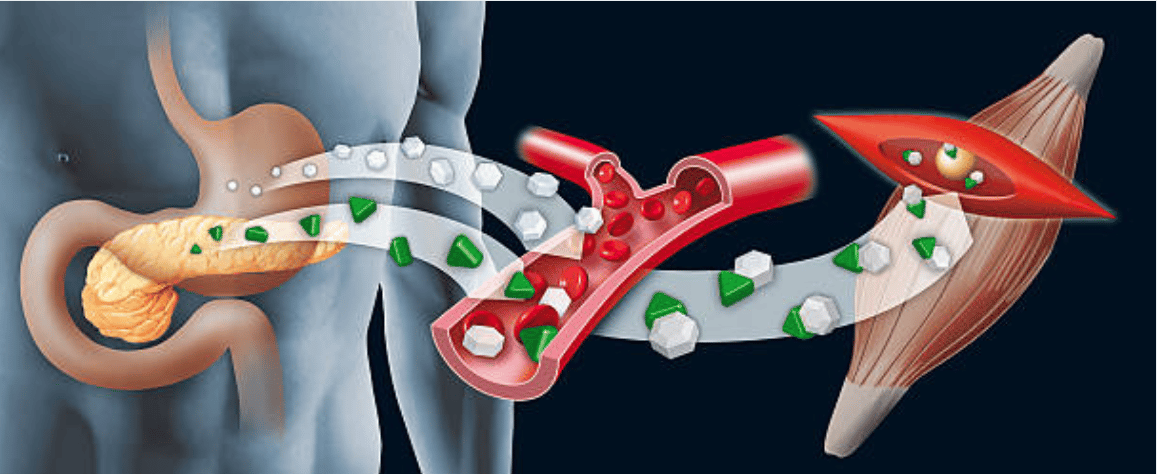
When you do a sport activity, your muscles need energy. Linked together by our precious joints, this mechanical energy allows them to perform the countless movements that the human body allows.
This fuel comes from the diet. It is brought by the carbohydrates (glucose), lipids (fatty acids) and proteins. This is why it is important to adopt a healthy and varied diet on a daily basis.
On the other hand, a diet that is too sweet or too high in calories can cause chronic fatigue and many other health problems.
Once stored in the body, this chemical energy is transformed into mechanical energy by the muscles, thanks to our famous glycogen.
Glycogen is a complex carbohydrate which is found in the liver as well as in the muscles. It is in fact a large molecule, composed of smaller glucose molecules.
Glycogen therefore has the capacity to store energy not used by the body for later use.
This is exactly what happens during a physical exercise. When the muscles need glucose to produce an effort, the body automatically dips into the glycogen reserves. This complex process is called glycogenolysis.
In any sport, energy is the source of performance. Without it, you will be forced to slow down or stop. Your glycogen level is therefore essential. If it is sufficient, everything goes well. If it's not, you won't have any gas left in the engine.
What happens when glycogen stores are depleted?
Your glycogen stores are emptied and refilled as you exercise and eat.
The glycogen degradation is done in a progressive way. It is conditioned in particular by the level of intensity and duration of the activity.
Your glycogen reserve will be depleted after :
- 90 minutes of sports activity at 75 % of your VO2 max (maximum oxygen consumption);
- or 4 hours of sports activity at 55 % of your VO2 max.
To counter this lack of glycogen, another source of energy comes into play and allows you to recover energy: lipids.
Lipids are the fats contained in our body and in our food. Contrary to popular belief, they are also important energy reserves for our body.
At the same intensity, a prolonged effort uses a mixture increasingly rich in lipids and amino acids. The muscle breaks down the glycogen in the liver and the fatty acids in the adipose tissue. The body, on the other hand, saves its glycogen stock. The glycogen contained in the muscles is converted into glucose.
But what happens if the glycogen level is completely depleted?
A lack of this energy source is directly detected by your brain, which acts as a switch.
This one transmits you a message to stop your sport activity. You can no longer continue, because you feel too tired and your motivation disappears. Runners know this feeling well. It is a phenomenon called " marathon wall ".
In summary, the depletion of glycogen in the body contributes to a decrease in your ability to provide a physical effort intense.
Be careful not to confuse this fatigue induced by a lack of energy in the form of glycogen with muscle fatigue. The latter can occur when your muscles suffer damage during their contraction, particularly during a very intense weight training session. Your effort can also be stopped, even if your will is still there, simply because your muscle can no longer continue.
The role of glycogen for bodybuilders
Now that you know what glycogen is, let's see how you can use it in your bodybuilding practice to help hypertrophy.
As we have seen, the amount of carbohydrates consumed during an effort depends on both its intensity and duration. The carbohydrate metabolism will be solicited during a very intense physical activity. On the contrary, during a lower intensity exercise, it is the aerobic process that acts. The latter will primarily use your sugar, fat and protein reserves.
To improve your sports performance, it is in your best interest to increase your glycogen stores. Indeed, they determine the duration during which you can perform an intense effort. To do this, two parameters must be taken into account: diet and training.
The diet
Your diet plays an essential role in optimizing your glycogen level.
Before a weight training session or a sporting event, make sure you take care of your diet to fill your body with energy. energy reserves. Indeed, the initial state of your glycogen stocks is important.
Choose foods that will not disturb your digestion. But be careful to the glycemic index of each food!
During a training session, energy is mainly provided by glycogen from your daily meals. This supply provides energy for 60 to 90 minutes depending on your starting stock. Beyond that, your reserve is exhausted and your performance decreases.
To compensate for this lack, you will need a energy intake You can also opt for carbohydrate-rich foods such as bananas, dried fruit or fruit compotes. You can also opt for carbohydrate-rich foods such as bananas, dried fruit or compotes.
After the effort, it is also essential to consume carbohydrates, because they are essential nutrients that participate in the resynthesis of glycogen. Therefore, they promote the development of muscle mass and physical recovery.
This post-training period of a few hours during which you must ensure your carbohydrate intake is called the anabolic window.
Various foods can help you replenish your glycogen stores:
- fruits and vegetables, thanks to their carbohydrate content;
- dairy products, as they contain essential amino acids;
- foods that promote the absorption of fast sugars, such as honey or energy bars;
- slow sugars, rich in starch;
- oilseeds (almonds, hazelnuts, cashews, pistachios, etc.), rich in vegetable proteins;
- oatmeal.
You can also prepare a protein shake with whey protein and maltodextrin, a powder made of carbohydrates from corn, wheat, potato or rice.
More broadly, a balanced diet is a major factor for a good carbohydrate recharge.
Sports training
The way you work out at the gym also affects how much glycogen you can store.
The more you exercise, the more you improve your insulin sensitivity. This will allow you to increase your glycogen stores and improve your performances.
How to use glycogen for bodybuilding competitions?
Emptying glycogen reserves voluntarily is a practice well known to bodybuilders. This is the principle of the carbohydrate rebound.
Before a competition or a photo shoot, the carb rebound allows bodybuilders to show a better physique. This practice is thus rather reserved for those who make of the competition.
A carbohydrate rebound occurs after a dryer.
During the dry period, athletes are looking to lose weight. They progressively decrease their carbohydrate intake in their diet (unlike during the muscle mass gain phases). This is the price to pay for a dry and muscular body during the competition.
Reducing this carbohydrate consumption mechanically leads to a decrease in the glycogen stock. Visually, this causes a degradation of the physical aspect. Muscles are less voluminous, which can cost valuable points in the final ranking.
The carbohydrate rebound consists precisely in suddenly increasing the quantity of carbohydrates in the body a few days before the competition, by playing on the volume of subcutaneous water. In this way, the muscles will temporarily appear more imposing.
Setting up a carbohydrate rebound before a competition is not easy. That's why I've prepared a full program of a week to approach your competition in the best possible conditions.
To conclude
Understanding how glycogen works in the body is a real asset for bodybuilders and other athletes. This molecule is our main source of fuel. And it is precisely by increasing your stock of muscle glycogen that you will be able to increase your performance.
Other articles to read :
What is the importance of blood sugar in weight training?