When we practice bodybuilding, movements are the result of the physical activity of the various muscles of the human body made up of myofibrils. These form the muscle fibres that play an essentially motor role in the coordination of body movements and thus allow for muscle building, strength gain and sometimes even endurance. Muscles are grouped into clusters, which may or may not contract when stimulated.
The ability to relax and contract muscles determines the mobility of the body. This ability of the muscle cells is the basis of strength training as a sporting activity. The latter, undertaken in a continuous and regular manner, contributes to muscle mass gain, thus increasing the power and performance of the athlete. In order to optimize a weight gain It is important to know the names of the muscles and their grouping according to the human anatomy.
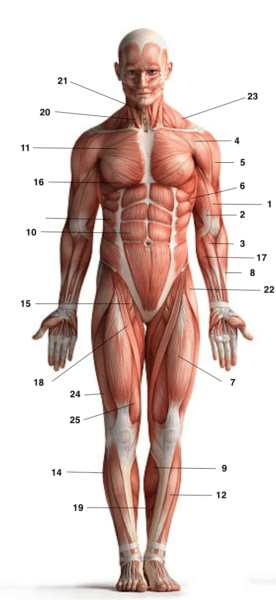
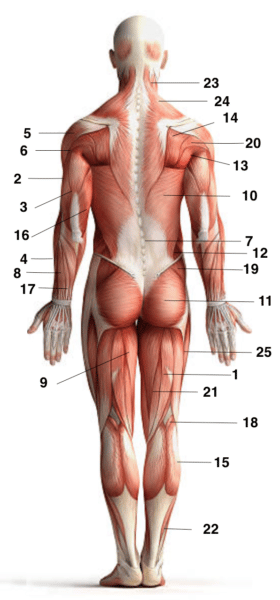
Here is a diagram of some of the main muscles of the body
- Biceps
- Brachial
- Brachio-radial
- Deltoid anterior bundle
- Deltoid external beam
- Anterior serration
- Femoral right of the quadriceps
- Ulnar extensor of the carpus
- Gastrocnemius
- Great rectus abdominis
- Great pectoral
- Anterior leggings
- Long fibular
- External oblique
- Pectinated
- Small pectoral
- Pronator round
- Sartorius - designer muscle
- Solar
- Sterno cleido mastoid
- Sterno hyoid
- Fascia lata tensor
- Trapeze
- External vastus of the quadriceps
- Internal vascular of the quadriceps
- Biceps femoris
- Lateral head of the triceps
- Medial head of the triceps
- Posterior ulnar
- Deltoid external beam
- Deltoid posterior bundle
- Spine erector
- Ulnar flexor of the carpus
- Adductor magnus
- Larger dorsal
- Large buttocks
- Big slant
- Large round
- Infra thorny
- Twins
- Long head of the triceps
- Long supinator
- Popliteal muscle
- Small buttocks
- Small round
- Semi-tendinous
- Solar
- Sterno cleido mastoid
- Trapeze
- Large external
Muscles of the body: roles and importance
It is necessary to know your muscular anatomy before doing any weight training. Not all the muscles in the human body have the same functions and are not used during physical exercise. In total, there are 639 muscles, 570 of which are striated muscles (skeletal muscles and smooth muscles in the human body).
Some striated muscles are the object of physical training and will be the subject of a brief presentation above from an anatomical board and a diagram of the human body. We have the names of the following muscles of the human body: pectorals, deltoids, trapezius, biceps and triceps, dorsal muscles, quadriceps, glutes, abs, forearm, calves and hamstrings.
From a brief description, we have :
The pectorals: They line the front part of the rib cage. They facilitate the crossing of the arms on the thorax, the movements of flexion and extension as well as the rotation of the arm.
The deltoids: covering the shoulder on the external side, they are essential in maintaining the arms in a forward or backward position.
The trapezius : They are part of the shoulder, are involved in the movement of the arms and allow the head to nod.
The biceps and triceps They are composed of bundles (long and short) and are supported by the shoulder and elbow. They play a central role in the flexion and release of the forearm. They are antagonistic muscles.
The dorsal muscles: They cover the thoracic cage and support the movements in the background of the arms.
The quadriceps femoris: located at the front of the thigh, it allows the hip to flex. It is composed of the vastus medialis, vastus lateralis, rectus anterior and crural.
The glutes: They are made up of the small, medium and large glutes. These three powerful components stretch the hip and tilt the pelvis backwards. The gluteus maximus is the largest and most powerful muscle in the human body..
We continue with
The abdominal muscles: They are composed of deep and superficial muscles. They cover the thoracic cage up to the pubis. They are involved in the stability and maintenance of the pelvis, the spine and the chest.
The forearm: It is made up of three types of muscle (long, short and flat). It helps to move the wrist and the hand.
The calves: They are a muscle of the leg. They run from the hock to the Achilles tendon. Are composed of three muscle bundles including the soleus and the twins. They ensure the movements relative to the foot.
Hamstrings: They run between the hip and the knees. They contribute to the movement of the knees and are essential for standing.
The adductors: characteristic of the thighs, they intervene in the movements of extension, flexion and rotation of the hip.
The intercostal muscles: They are located between the ribs and support the rib cage. They also facilitate respiratory movements.
They gather in groups in which the synergy of their function satisfies the expressed needs for mobility. If you are not a beginner, one training per week and per group is recommended.
What is a muscle group?
A muscle group is a set of muscles in the body that work together to make movements whose functionality contributes to the same physical response. They are attached to the same joints and are therefore considered a single muscle group.
As a good example, the arms contain the following muscles: biceps brachii, triceps brachii and anterior brachii which can be worked together.
The different types of muscle groups
Generally speaking, there are two categories. These are the primary and secondary groups. Such a classification only takes into account the main muscles, because it is unlikely that all the different muscles of the human body can be divided into groups.
The primary group contains:
- Chest
- Back
- Quadriceps
- Ischio
The secondary group contains:
- Shoulders
- Biceps
- Triceps
- Calves
More specifically, there are also 5 groups and these are: the lower group, the upper group, the shoulder girdle, the abdominal wall and the back wall.
The lower group includes :
- the gluteus maximus, which is made up of three muscles: the gluteus maximus responsible for the convex shape of the buttocks, the gluteus medius and the gluteus minimus. It is one of the most important in terms of power and mass. It is involved in the stability of the hip and the movements of the thighs.
- the abductor, which maintains the distance between a body member and the median axis
- the adductor, which maintains a movement of approach between a limb of the body with the median axis
- the hamstring, which ensures the movements of flexion of the knee and extension of the femur. It is in antagonism with the quadriceps
- the femoral quadriceps, also known as the quadriceps crural, which is large and provides excellent support for the body's weight. It is the origin of the motility of the feet
- the twins represented by the calves which are involved in the extension movements of the ankle.
The top group includes :
- the biceps and triceps which respectively ensure the movements of flexion and extension of the elbow. Both function in an antagonistic way to allow the movements of the arms
- the flexor and extensor of the forearm.
The scapular belt includes:
- the trapezius which are essential for the lifting movements of the shoulders and consequently for the convergence of the shoulder blades
- the pectoralis major, which is responsible for lowering the arms by bringing the shoulders together
- the deltoid muscle helps to spread the shoulders in order to lift the arms
- the great dorsal specialized in the movements of stretching of the arm in front or behind.
The abdominal wall is composed of:
- the obliques, which are responsible for the flexion and rotation of the pelvis and the torso
- the rectus abdominis, which ensures the flexion movements of the trunk in relation to the pelvis.
The back wall consists of:
- The back extensor which is the main support for the backward movement of the arms.
How many times a week should I work the same muscle group?
When we are beginners, depending on the equipment available, it is important to start by working all the muscles in one day, or half the body (upper body or lower body). This is called the full body and half body.
If you have equipment or go to a gym, you can start with the half body.
If you do not have any equipment, it is recommended that you follow a bodyweight program.
When we gain experience and are a minimum of experienced, then we can move on to a program in split(one muscle group per day).
It should be noted that the group to be worked during the sessions depends on your training program, but whatever the program you follow, you will have to work on one or more muscle groups.
It also depends on the increase in muscle mass. The more advanced you are, the more your muscles will require more intense and specific exercises related to one or more groups. It is therefore advisable to organize your weight training sessions and physical exercises according to muscle groups for greater efficiency in order to avoid generalized body fatigue and to continue your progression.
In summary, it depends on your experience and your training program but it is advisable not to work the same muscle group twice in a week. It is still possible to do an encore, but make sure you have recovered enough in terms of rest. A minimum of 3 or 4 days after.
Find out more here: Five facts about muscles in the human body: An overview of muscles and their movements
You now know a little more about the muscles and muscle groups, you just have to follow a good training program according to your goals.
Remember that it is not enough to train to gain muscle, you must also integrate a diet in line with your practice of bodybuilding.
Additional articles :
What is the purpose of the deep muscles?
What exactly is muscle hypertrophy?











4 Comments
hello julien i started reading but you lost me along the way some things interesting but others too complicated
I go to the gym and I push, period, but I appreciate your effort to teach us
really super technical and even a little too much for me too on the other hand could you make us a video or an article on the short and long muscles just to have your opinion, sporty, daniel
really super technical and even a little too much for me too but could you make us a video or an article on short and long muscles just to have your opinion, sportivly, daniel
Thanks! It's a good idea to video the long and short muscles even if we can't do much against genetics...